|
|
ExposureIn photography, exposure is the amount of light per unit area reaching a photographic film or electronic image sensor, as determined by shutter speed, lens aperture and scene luminance. Too much exposure will end up to overexposed, a condition where the photo seems washed out, and to less exposure will end up to underexposed, a condition where the photo seems dim and dark.
ApertureIn photography and digital photography, aperture is the unit of measurement that defines the size of the opening in the lens that can be adjusted to control the amount of light reaching the film or digital sensor. When the aperture value is low, the opening size is larger and this will end up to blurry background. When the aperture value is high, the opening size is smaller and will result to sharp focused image.
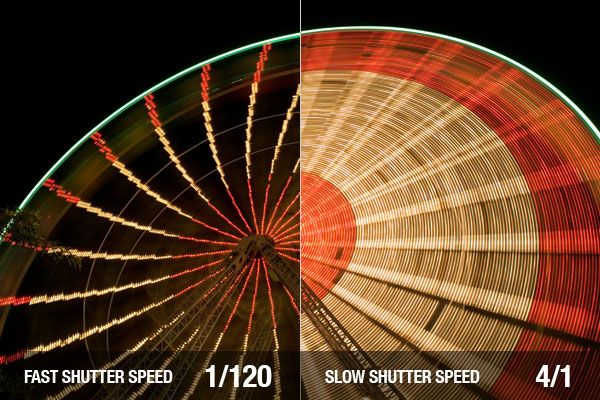
Shutter SpeedIn photography, shutter speed or exposure time is the length of time when the film or digital sensor inside the camera is exposed to light, also when a camera's shutter is open when taking a photograph. Faster shutter speed, will result to a still image of a moving one. A slower shutter speed will gave you the movement image of the subject.
CompositionComposition is a way of guiding the viewer’s eye towards the most important elements of your work, sometimes – in a very specific order. A good composition can help make a masterpiece even out of the dullest objects and subjects in the plainest of environments. On the other hand, a bad composition can ruin a photograph completely, despite how interesting the subject may be.
Rule of ThirdThe rule of thirds is a "rule of thumb" or guideline which applies to the process of composing visual images such as designs, films, paintings, and photographs. The guideline proposes that an image should be imagined as divided into nine equal parts by two equally spaced horizontal lines and two equally spaced vertical lines, and that important compositional elements should be placed along these lines or their intersections. Proponents of the technique claim that aligning a subject with these points creates more tension, energy and interest in the composition than simply centering the subject
Depth of FieldIn optics, particularly as it relates to film and photography, depth of field (DOF), also called focus range or effective focus range, is the distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. The depth of field is determined by the aperture of the lens being used. The lower your f-number, the smaller your depth of field. Likewise, the higher your f-number, the larger your depth of field.
BalanceBalance is a photography technique that involves capturing images within a frame so all parts of the image have equal visual weight. Proper balance should increase the visual appeal of a photograph. There are generally two types of balance, formal and informal Formal balance is symmetrical balance. To achieve this type of balance, the focus of the picture should be placed in the middle of the image, while identical or similar subjects are evenly spaced around the central point. Portraits are an example of a picture where it is best to use formal balance. Informal balance is more indistinct in nature. In a photograph with informal balance, dissimilar elements balance each other out on either side of the frame. Informal balance can occur with objects of any size, but it is most visually appealing to have a larger object balanced out with a smaller object or several smaller objects. This type of balance usually follows the rule of thirds. Other ways to informally balance photos include having a small area of white against a large area of black, or black against white. This principle also works with vibrant colors against neutral colors. A small area of highly textured material can also balance out an area with little texture. |